請點擊這裡查看中文版
In the previous article ” Green Building Assessment Aspects”, we have mentioned that our local green building assessment tool – BEAM Plus (New Building, version 1.2) covers SIX aspects, including Site Aspect/ Sustainable Site (SA/SS), Materials and Waste Aspects (MA/MWA), Energy Use (EU), Water Use (WU), Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ)and Innovations and Additions (IA). (Note: NB version 2.0 also includes Integrated Design and Construction Management (IDCM), IEQ also renamed “Health and Wellbeing (HWB)”).
Today, I would like to introduce one of the credits under Materials Aspects (MA/MWA): MA 9 (NB 1.2)/MWA 8 (NB 2.0) – Regionally Manufactured Materials. This credit requires that at least 10% (1 point) of all building materials in each project should be extracted (raw materials) and manufactured regionally (2 points for more than 20%) while the purpose is to reduce environmental impacts arising from transportation and support the regional economy.
The following will share with you:
1) What building materials should be considered in the green building assessment?
2) How do we define “regionally”?
1) What building materials should be considered in the green building assessment?
The construction stages of a building are divided into demolition, foundation, and superstructure. Generally, the foundation phrase only includes the use of concrete and steel, while the superstructure uses thousands of materials in different construction works: structural framework (e.g. concrete and steel), facade (e.g. windows and cladding), and internal works (e.g. doors, built-in furniture, paint, partition walls).
According to the BEAM Manual, the assessment should consider all building materials, but excluding materials used in plumbing works. However, due to the huge number of materials involved in constructing a building, we usually include major building materials (e.g. concrete, steel, doors, curtain walls) in the assessment. (Note: In NB 2.0, concrete cannot be counted in the assessment).
Kindly be reminded that the unit may be mass/volume/dollar but it should be consistent throughout the assessment of this credit.
2) How do we define “regionally”?
According to the BEAM Manual, “regionally” is defined as: the point of raw materials and manufacture should be located within an 800km (i.e. 500 miles) radium by road transportation. Under NB 2.0, it will also consider the point within a 1,600km radius by rail transportation; or within a 4,000km radius by sea transportation.
Knowing that everyone may not have an idea of what countries/cities should be covered within 800 km/1,600 km/4,000 km from Hong Kong, so I have prepared the following maps for better understand.
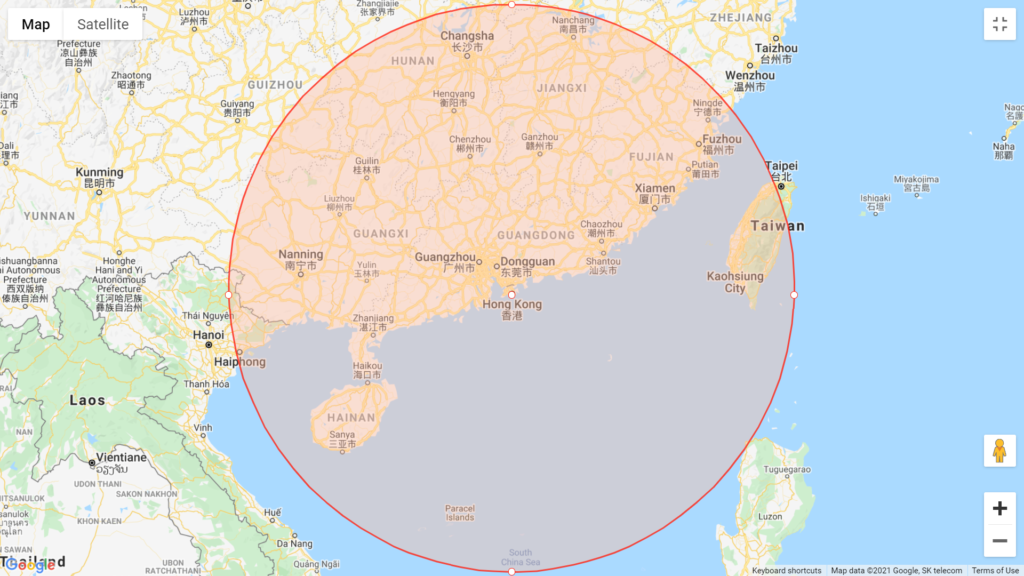
• Basically 800 km includes Guangdong, Dongguan, Nanning, Changsha, Xiamen, Hainan and most of Taiwan.
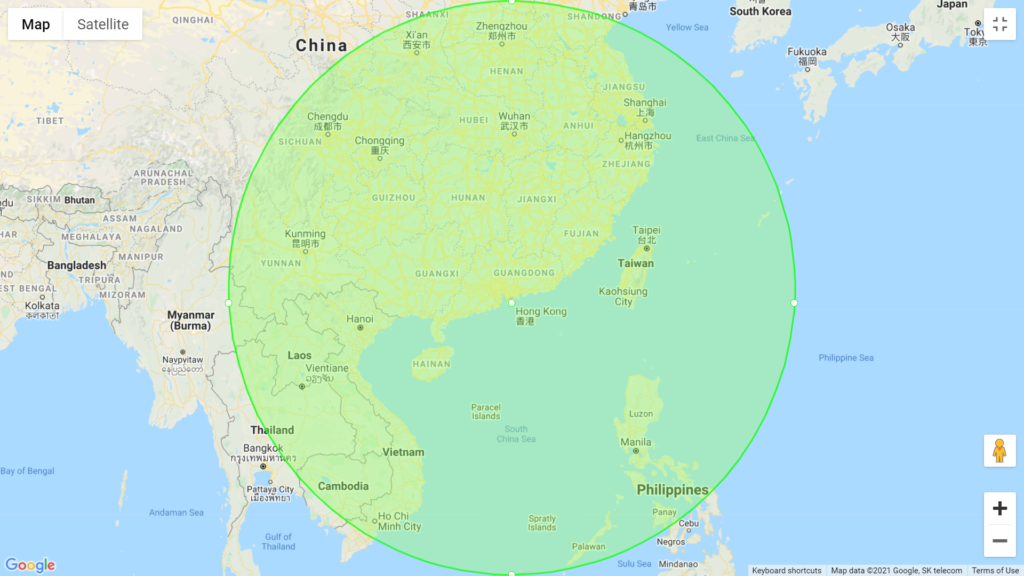
• The 1,600 km covers Shanghai, Hangzhou, Wuhan, Chengdu, Chongqing, Kunming, Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia and Manila.
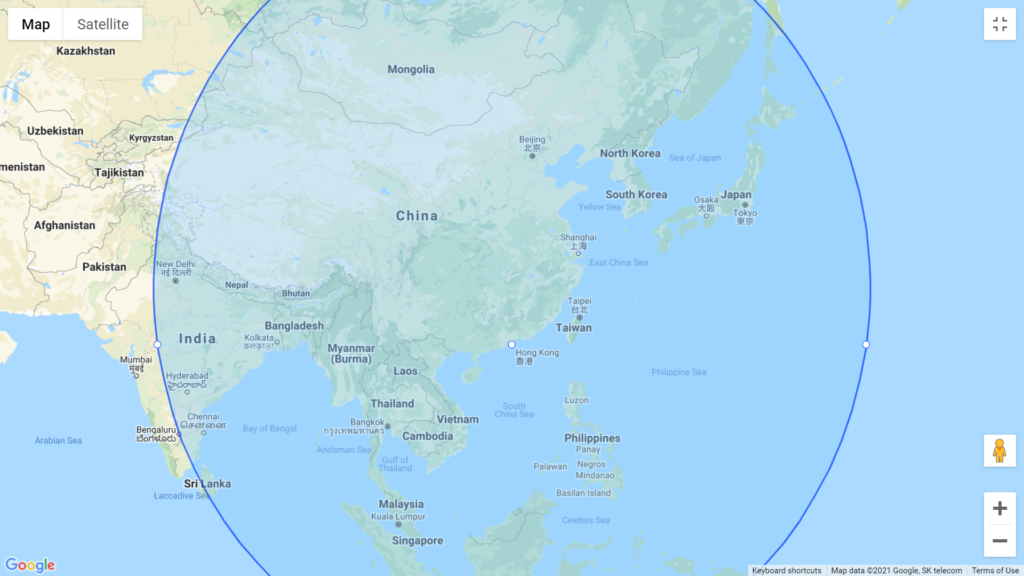
• The 4000 km extends to South Korea, Japan, the Philippines, Singapore, Malaysia and parts of India.
Map 1: Countries/cities within 800 km from Hong Kong
Map 2: Countries/cities within 1600 km from Hong Kong
Map 3: Countries/cities within 4000 km from Hong Kong
Discussion:
1. If you live in Hong Kong, when you decorate your home or buy new furniture, would you consider to use products from 800 km?
2. If you live in other places, can you share with us what countries/cities will be covered within 800km from your home?
Reference
https://www.beamsociety.org.hk/files/download/download-20130724174420.pdf
https://www.beamsociety.org.hk/files/download/NBv2_0_2021_FinalVersionR.pdf





0 Comments